If you’ve ever watched a science fiction movie where someone opens a cryogenic tank to reveal a frozen specimen, you’ve probably encountered a Dewar flask, even if you didn’t know it at the time. Whether you’re in a lab, a hospital, or even working in a food processing plant, Dewar vessels play a pivotal role in storing gases at extremely low temperatures—keeping them stable, safe, and ready for use.
A Dewar vessel is a container used to store gases and liquids at extremely low temperatures. Invented by James Dewar in the 1800s, it features double-walled insulation to reduce heat transfer. Dewar vessels are essential in medical, industrial, and scientific fields for storing substances like liquid nitrogen and oxygen. Modern versions are more durable and efficient, but safe handling is crucial.
So, what exactly is a Dewar vessel, and why is it so crucial? Let’s dive in.

A Dewar flask, also known as a Dewar vessel, is a specialized container designed to store and transport gases and liquids at extremely low temperatures. It consists of a double-walled container with a vacuum or insulating material between the walls, which minimizes heat transfer and helps maintain the low temperature of cryogenic substances like liquid nitrogen, oxygen, and helium. Dewar flasks are widely used in scientific, medical, and industrial applications that require the preservation of substances at cryogenic temperatures.
History of the Dewar flask
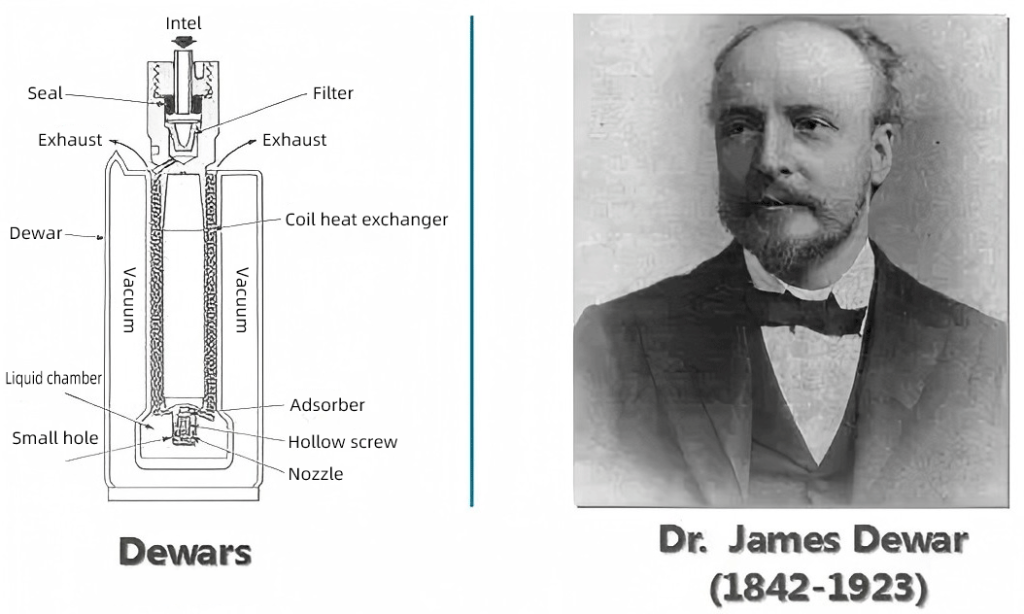
To understand the significance of Dewar vessels, we have to rewind to the late 1800s. Enter James Dewar, a Scottish scientist with a knack for exploring the extremes of temperature. Dewar wasn’t just playing with liquid nitrogen for fun—he was conducting serious experiments in cryogenics, a field that explores the behavior of materials at ultra-low temperatures.
Dewar invented the vessel that bears his name around 1892. Initially, his goal was to create a container that could hold liquefied gases, which, at the time, were incredibly tricky to manage. Through the use of double-walled flasks and a vacuum between the walls (a method we still use today), Dewar successfully invented a container that reduced heat transfer—keeping the gases inside stable at incredibly low temperatures.
Fast forward to today, and Dewar vessels are used in everything from storing medical gases like oxygen to cryogenically preserving biological samples. James Dewar, though long gone, still influences the way we store and transport gases for research, medical treatment, and industrial processes.
Common Gases Stored in Dewar flasks
Now, what do Dewar vessels actually store? Well, quite a variety of gases, all of which have unique properties when cooled to liquid form. Let’s look at some of the common ones:
· Liquid Oxygen (LOX): Widely used in hospitals and healthcare facilities for respiratory treatments, LOX is also a vital component of rocket propulsion. That’s right—this cold gas helps launch rockets into space!
· Liquid Nitrogen (LN2): The workhorse of the cryogenic world. It’s used in everything from cryopreservation (think frozen embryos) to food freezing (liquid nitrogen ice cream).
· Liquid Argon (LAR): Mainly used in industrial settings like welding or steel production, this gas is as essential as oxygen, though much less talked about.
· Liquid Helium (LHe): This is the ultra-cold superhero, chilling down to temperatures close to absolute zero. It’s used in MRI machines and other high-tech applications, like supercooling superconductors for scientific experiments.
· Other Gases: While oxygen, nitrogen, and helium get the most attention, there are other gases like CO2 and LNG that also benefit from being stored in Dewars.
Safety Considerations in Using Dewar flasks
Cryogenic gases, while useful, can pose real dangers if mishandled. Let’s go through the basic safety precautions every user should follow:
Wear Protective Gear: Cryogenic liquids are extremely cold, which means they can cause severe cold burns if they come into contact with skin. So, gloves, goggles, and a face shield are a must when handling Dewar vessels. And yes, a lab coat is your friend here too.
Storage Location: Dewar vessels should be stored in well-ventilated areas. As gases like liquid nitrogen vaporize, they expand rapidly. In confined spaces, this can lead to a dangerous buildup of gas, potentially displacing oxygen in the room. This can cause suffocation, so always prioritize ventilation.
No Spilling Allowed: A spilled cryogenic liquid can evaporate quickly and cause localized cooling that could damage surfaces or even lead to cracking in other materials. In the event of a spill, immediately evacuate the area and follow proper emergency procedures.
Pressure Build-Up: Liquid gases stored in Dewar vessels are always trying to turn back into their gaseous forms. If the vessel is closed off without a proper vent, the pressure inside can build up rapidly. This can lead to dangerous situations, like explosions. Always make sure that the Dewar vessel has a proper venting mechanism.
While these may sound like common-sense precautions, they are essential for anyone working with Dewar vessels. Cryogenic materials are not to be taken lightly, and it’s critical to understand their risks.
Operating Recommendations
Dewar vessels are generally pretty low-maintenance, but there are still a few tips and best practices to keep them running smoothly:
Check for Leaks Regularly: Make sure to inspect Dewar vessels for any potential leaks. Cryogenic liquids can easily escape through tiny cracks or faulty seals, so keeping an eye on the vessel’s integrity is important for safety and efficiency.
Keep the Vessel Upright: Dewar vessels should always be kept upright when in use or during transportation. Tilting a Dewar vessel may cause the liquid to splash out, which could lead to accidents.

Temperature Control: While Dewar vessels are designed to minimize heat transfer, sudden temperature fluctuations can still lead to thermal shock. Be mindful of your environment and avoid moving the Dewar vessel from extremely cold areas to warmer spaces too quickly.
Regular Inspections: While Dewar vessels are built to last, regular inspections are necessary to ensure they continue to operate at peak performance. Inspect the seals, the insulation, and any valves or vents to make sure everything is working as it should.
Technological Advancements in Dewar Design
Let’s talk about technology! Dewar vessels have come a long way since James Dewar’s original design. While the basic principle has remained the same—insulate and store gases at extremely low temperatures—modern Dewar vessels have seen a number of improvements:
Vacuum Insulation: This method minimizes heat transfer and keeps gases cold for extended periods.
Improved Durability: Newer models are made with more durable materials that are designed to handle rougher conditions, particularly in industrial applications where the Dewar vessel may face frequent movement or high-pressure environments.
Smaller, More Efficient Models: As technology advances, Dewar vessels have become more compact, making them more convenient for specific use cases like laboratory research or medical transport.
Applications of Dewar Vessels
So, where are these vessels used?
Medical and Healthcare: Dewar vessels are indispensable in the healthcare sector for storing and transporting blood, vaccines, and other biological materials that need to be kept at extremely low temperatures.
Industry: Dewar vessels are also used in manufacturing processes that require cryogenic conditions, such as semiconductor production, metalworking, and even food freezing.
Scientific Research: In laboratories, Dewar vessels keep gases for experiments that explore everything from low-temperature physics to cryogenically preserving samples.
Aerospace: NASA and other space agencies rely on Dewar vessels to store liquid oxygen and other cryogenic fuels for rockets and space shuttles.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Dewar Vessels
As you can see, Dewar vessels play a critical role in various industries. They’re not just some fancy laboratory equipment; they are fundamental tools that allow us to work with gases at extremely low temperatures. Understanding their history, proper handling, and technological advancements helps ensure that we’re using them safely and efficiently.
So, the next time you see a Dewar flask, remember: it’s more than just a cool container. It’s a vital piece of equipment that makes modern science, medicine, and industry possible.
If you want to know more, you can visit our official website. We will answer your questions and provide reliable solutions at any time!